With the development of the low-altitude economy, drones have permeated various industries, helping to reshape industrial ecosystems and promote industry transformation with new technologies. Do you know the specific application scenarios of drones? Let’s introduce them in detail below.
1. Agriculture
Farmland Monitoring: By carrying high-definition cameras or multispectral sensors, drones can regularly patrol farmland to monitor crop growth status (such as leaf health, pest and disease conditions), soil moisture and fertility distribution, providing data support for precision agriculture. For example, multispectral imagery can identify areas lacking water or fertilizer, helping farmers take timely measures.
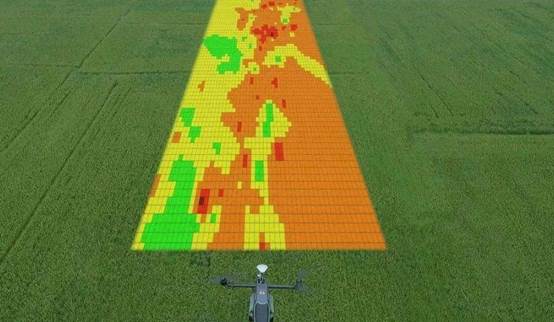
Sowing and Fertilizing: Drones equipped with sowing devices can evenly sow seeds in large areas of farmland, improving sowing efficiency; at the same time, based on farmland monitoring data, they can accurately and quantitatively apply fertilizers, reducing fertilizer waste and environmental pollution.
Pesticide Spraying: Drone spraying of pesticides is highly efficient and provides even coverage, especially suitable for farmland with complex terrain or large areas, reducing manual labor intensity and the harm of pesticides to humans.

2. Logistics and Transportation
Express Delivery: In remote areas or places with inconvenient transportation, drones can quickly deliver packages, shortening delivery time. For example, some logistics companies have tried using drones to provide express delivery services to mountainous areas and islands.
Material Transportation: After natural disasters (such as earthquakes and floods), when roads are blocked, drones can transport emergency supplies (such as food, medicine, and drinking water) to disaster areas, saving time for rescue work.

3. Aerial Photography and Film Production
Aerial Surveying and Mapping: Drones equipped with high-precision cameras and GPS devices can perform aerial surveying and mapping of terrain, buildings, and construction sites, generating 3D models and maps, which are widely used in urban planning, land surveying, and engineering construction. For example, in construction projects, drones can regularly photograph construction progress, helping construction companies to monitor project progress.
Film and Television Production: Drones can capture unique camera angles (such as low-altitude flyovers and high-altitude view), providing rich visual effects for movies, TV series, and documentaries, especially suitable for shooting large scenes or dangerous shots, reducing shooting risks and costs.

4. Environmental Protection and Monitoring
Ecological Monitoring: In nature reserves, drones can monitor the activity patterns, population size, and habitat conditions of wild animals, helping researchers and conservation organizations better protect endangered species. For example, thermal imaging cameras can be used to monitor animal distribution at night.

Environmental Monitoring: Used to monitor air quality, water quality, and forest fire hazards. For example, drones equipped with gas sensors can detect whether industrial exhaust emissions exceed standards; in forests, infrared sensors can be used to detect potential fire points and provide timely warnings.
Marine Protection: Monitoring marine ecosystems (such as coral reefs and marine mammals), while also tracking and combating illegal fishing activities to protect marine resources.
5. Infrastructure Inspection and Maintenance
Power and Communication Line Inspection: Drones can inspect high-voltage transmission lines and communication base station towers, detecting faults in the lines (such as broken wires, damaged insulators), and corrosion of the towers, which is safer and more efficient than manual inspection.

Bridge and Building Inspection: Inspecting the structure of bridges and high-rise buildings to check for cracks, leaks, and other problems, and promptly identify safety hazards. For example, drones equipped with laser scanners can accurately inspect the three-dimensional structure of bridges.
Oil and Gas Pipeline Inspection: Flying along pipelines to detect leaks and assess whether the surrounding environment poses a threat to the pipelines (such as construction damage, soil erosion, etc.).
6. Public Safety and Emergency Rescue
Disaster Relief: At disaster sites such as earthquakes, fires, and floods, drones can quickly obtain images of the affected area, helping rescue workers understand the distribution of the disaster, the number of affected people, and the location of trapped individuals, and develop rescue plans. They can also deliver life-saving equipment or transmit information.
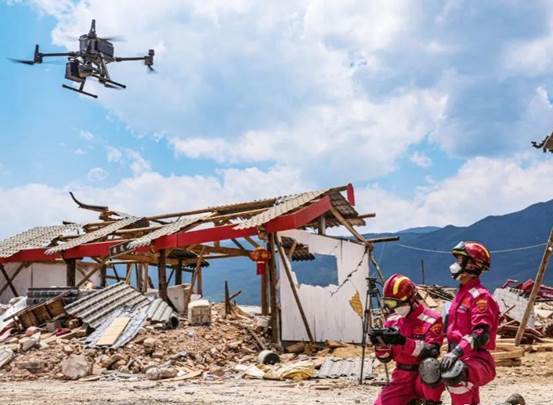

Security Patrols: Used for urban security patrols, monitoring traffic conditions, apprehending suspects, or searching for missing persons. For example, during large events, drones can monitor crowd movement from the air to prevent stampedes and other accidents.
Border and Coastline Patrols: Patrolling border areas and coastlines to prevent illegal border crossings and smuggling, improving border management efficiency.
7. Scientific Research and Education
Scientific Research: In fields such as atmospheric science, geology, and biology, drones can be used to collect data. For example, in meteorological research, drones can fly into clouds to measure meteorological parameters; in geological exploration, they can obtain high-resolution images of geological structures.

Education and Training: As a teaching tool, drones help students learn aviation knowledge, programming control, and sensor technology, fostering technological innovation capabilities. Many schools and training institutions have already launched drone-related courses.
8. Commercial and Consumer Fields
Performance and Promotion: Businesses can use drones for advertising and promotion, such as performing drone formations at events to attract public attention; or shooting corporate promotional videos to showcase corporate strength and product features.

Personal Entertainment: Consumer-grade drones, due to their portability and ease of use, have become toys for photography enthusiasts and technology enthusiasts, used for shooting travel scenery, recording life moments, etc.
9. Other Fields
Archaeological Exploration: Through aerial photography and sensor technology, drones can discover traces of ancient underground sites, providing clues for archaeological research.
Medical Field: In emergency situations, drones can transport blood, organs, and other medical supplies, saving time for rescuing patients; in addition, they can be used for remote medical diagnosis, obtaining patient vital sign data through cameras and sensors.
Mining and Quarries: Drones can monitor the topography and reserves of mines and quarries, plan mining routes, and improve mining efficiency and safety.
With continuous technological advancements, the application scenarios of drones are constantly expanding, and they are expected to play an important role in more fields in the future.

Leave a Reply